Shared Features: Expression Builder
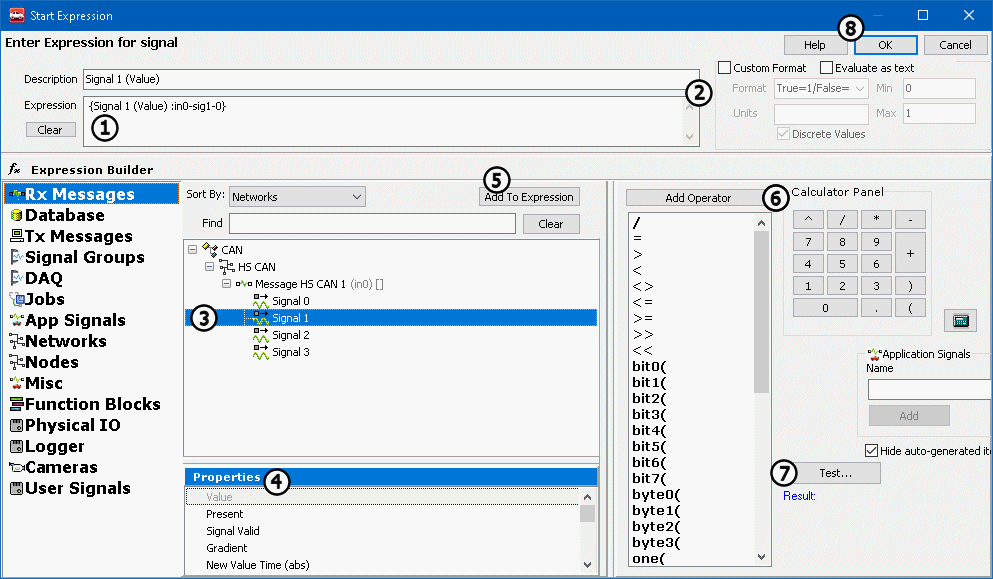
The Expression Builder is a handy feature that will be used again and again while working with Vehicle Spy. This user friendly dialog builds expressions for many tasks such as controlling Function Blocks, linking signals to Graphical Panel elements, and creating custom filters. The interface is constant throughout Vehicle Spy, so there is no burden of learning dozens of complicated dialogs. Just get familiar with the Expression Builder and that's it! Please refer to Figure 1 below as the features of this dialog are explained further.
Enter Expression Area:
Enter an equation directly into the Expression field at the top of the screen (Figure 1:![]() ). This field has a right click menu with standard editing features. Use Evaluate as text (located below the Expression field) for expressions containing only text, or a combination of text and pure data elements without operations performed on them. For example, the expression "The value of engine rpm is {Engine RPM :in1}" should have evaluate as text enabled. If an expression value will be displayed, use the Custom Format options (Figure 1:
). This field has a right click menu with standard editing features. Use Evaluate as text (located below the Expression field) for expressions containing only text, or a combination of text and pure data elements without operations performed on them. For example, the expression "The value of engine rpm is {Engine RPM :in1}" should have evaluate as text enabled. If an expression value will be displayed, use the Custom Format options (Figure 1:![]() ) to control its format and units, and min/max values.
) to control its format and units, and min/max values.
Expression Builder Area:
Vehicle Spy data sources are selected in the column on the far left. When a source is selected its data items will be displayed in tree form to its right (Figure 1:![]() ). When a data item is chosen its available properties are displayed just below the data item tree (Figure 1:
). When a data item is chosen its available properties are displayed just below the data item tree (Figure 1:![]() ). After you select an item and its property you can add it to the Expression field by clicking the Add to Expression button (Figure 1:
). After you select an item and its property you can add it to the Expression field by clicking the Add to Expression button (Figure 1:![]() ). Create more complicated expressions using the Add Operator and Calculator Panel functions (Figure 1:
). Create more complicated expressions using the Add Operator and Calculator Panel functions (Figure 1:![]() ) or by typing in the Expression field directly. After your equation is complete, it can be tested by clicking the Test button (Figure 1:
) or by typing in the Expression field directly. After your equation is complete, it can be tested by clicking the Test button (Figure 1:![]() ). The test result will display below. When you are finished building your expression, click the Ok button (Figure 1:
). The test result will display below. When you are finished building your expression, click the Ok button (Figure 1:![]() ) to return to the previous view.
Note that similar to C/C++ or Visual Basic, Boolean type equations are false when they evaluate to zero and true otherwise.
) to return to the previous view.
Note that similar to C/C++ or Visual Basic, Boolean type equations are false when they evaluate to zero and true otherwise.
Data Sources, Data Items, Properties, & Operators:
The Expression Builder has many data sources, data items, properties, and operators. Use Table 1 below as a navigation aid to jump to specific tables or related Help Topics.
Table 1: Data Source Jump Table
Below, Table 2 describes all of the different properties for the different data sources in the Expression Builder. Digital refers to a signal that can be on or off like a switch. Analog refers to a signal that can have many different values like Vehicle Speed.
Table 2: Data Source Properties
Message Properties: Rx Messages, Database, Tx Messages (shared)
Present
Digital
Turns true when message is first present on the bus.
Present Toggle
Digital
Toggles True/False every time the message appears on the bus.
Update Rate (rel)
Analog
Time between counts of this message.
Update Rate (abs)
Analog
Time this message appeared on the bus relative to when Vehicle Spy starts.
Per Second
Analog
Rate that the message appears on the bus.
Count
Analog
Number of times that the message appears on the bus.
Change Count
Analog
Returns the number of times the message has changed.
Start Time
Analog
Time that the message first appeared on the bus.
Min Time
Analog
Minimum update rate for the message.
Max Time
Analog
Maximum update rate for the message.
Mean Time
Analog
Mean update rate for the message.
Message Status
Analog
Status flags for the message.
Message ArbID
Analog
ArbID of a CAN type message as listed in the Messages Editor Rx/Tx/Database tables.
Message RTM Frame
Digital
True if the message was a remote frame.
Message PT
Analog
PT byte of the message.
Message Trgt
Analog
Trgt byte of the message.
Message Src
Analog
Src byte of the message.
Message Length
Analog
Number of data bytes in a single frame message.
Message B1 to B8
Analog
Data bytes B1 to B8 of the message.
Message Xtd ID
Digital
True if message has an Extended Arbitration ID.
Message Is Tx Msg
Digital
True if the Rx message was transmitted by Vehicle Spy. Simplifies network gateway logic versus using Has Transmitted because wildcard filters are allowed only on Rx messages.
MultiFrame (MF) Complete
Digital
True if multiframe message completed ok.
Message Data
Analog
Use this for efficient gateway functionality, but not for display purposes. Example: Msg1(Message Data) = Msg2(Message Data).
MultiFrame Flow Control Arb ID
Analog
Arb ID of the flow control frame in a multiframe message.
Message BX
Analog
Message data byte BX, where X = index. (Index 0 = byte B1, index 1 = byte B2, etc.)
Received Transport Layer Payload Length
Analog
Number of data bytes in a multiframe message.
Transport Layer Error Flag
Analog
Non zero values imply transport layer stack detected a problem.
Last Received Arb ID
Analog
Last received ArbID of a message in a Rx or Database table. This is typically the same value as Message ArbID, but not when wildcard "X" bitwise filters are being used in the Messages Editor.
Message Properties: Unique to Tx Messages
Any Tx Msg property shared with Rx Msg
n/a
Click HERE to go to start of Rx Message properties. (Tx Msg properties shared with Rx Msgs are explained there. Properties unique to Tx Msgs are explained here.)
Tx Msg Period Ms
Analog
Periodic rate for the message (in milliseconds).
Tx Msg Periodic On-Off
Digital
Periodic mode of the message (0-normal, 1-periodic).
Has Transmitted
Digital
Becomes true if the message is transmitted by Vehicle Spy.
Signal Properties: Rx Messages, Database, Tx Messages, DAQ, Jobs
Value
Any
Value AFTER the Messages Editor signal equation is applied. The signal type determines the property type.
Present
Digital
True if the message with the signal has been on the bus.
Signal Valid
Digital
True if the signal valid is current.
Gradient
Analog
Change in value between the last two instances of the signal.
New Value Time (abs)
Analog
Time that the last signal was received.
Start Value
Analog
Initial value of the signal.
Min Value
Analog
Minimum value received.
Max Value
Analog
Maximum value received.
Mean Value
Analog
Mean value of the received signal.
Start Gradient
Analog
Initial change in the signal's value.
Min Gradient
Analog
Smallest change in the signal's value.
Max Gradient
Analog
Largest change in the signal's value.
Mean Gradient
Analog
Mean value of the change in the signal's value.
Signal Group (Logging) Properties
Is Logging
Digital
True only when the signal group is currently being logged.
Log Count
Analog
Number of lines logged for the signal group.
Pre Log Count
Analog
Number of lines collected in the pre-start log buffer.
Time Remaining
Analog
Time remaining in the currently active signal group logging event (seconds).
Total Time
Analog
Total time of the signal group logging event (seconds).
DAQ Properties
Is Running
Digital
True when the DAQ is running.
Is Triggered
Digital
True when the DAQ is triggered.
Number Msgs Collected
Analog
Number of lines collected by the DAQ.
Job (Diagnostic) Properties
Is Running
Digital
True while the job is running.
Number Messages Collected
Analog
Reports total number of messages received during the job.
Is Successful
Digital
True if the job completed successfully.
ECU Response Count
Analog
Number of ECUs that responded to the job.
Total Time Abs
Analog
Total time used to complete the job.
Last 7F Sub Function Excluding 78
Analog
Last negative response sub-function received that was not a $78.
7F Count Excluding 78
Analog
Number of negative responses received excluding sub-function $78.
7F count 78 Response Pending
Analog
Number of negative responses received with sub-function $78.
Application Signal Data Items
Application Signal Name
Any
Value of the Application Signal. The data item type depends upon the application signal type. If the signal is in an array, use the index (starts at 0) to access elements within the array.
Network Properties
Count
Analog
Number of messages for the network.
Rate
Analog
Number of messages per second for the network.
Percent Use
Analog
Percent of network utilization for the network.
Max Rate
Analog
Maximum number of messages per second for the network.
Max Percent Use
Analog
Maximum network utilization for a network.
Error Count
Analog
Number of errors on the network.
Tx Count
Analog
Number of messages transmitted by Vehicle Spy on the network.
Error Rate
Analog
Number of errors per second on the network.
Tx Rate
Analog
Number of messages transmitted per second on the network.
Tx Buffer Fill
Analog
Number of messages in the transmit buffer of the connected hardware on the network.
Enabled
Digital
Enables the network. Some networks cannot be enabled at the same time (ex: LIN2, ISO2, and CGI on FIRE). Assigning a 1 will enable the network and disable other networks that would conflict.
Available
Digital
Read as 1 if network is available on current hardware, 0 otherwise. Useful for CoreMinis designed to run on several different 3G devices.
Fast Wakeup Enable
Digital
Enables Fast Wakeup (no missed messages) for the HSCAN or MSCAN networks. (CoreMini only) Note: neoVI hardware has more parasitic current draw when this is enabled.
Bitrate
Analog
Network bitrate in bits per second. Read value represents the current bitrate. Write to signal to change desired bitrate. Valid values for CAN are: 20000, 33333, 50000, 62500, 83333, 100000, 125000, 250000, 500000, 800000, & 1000000. Valid values for LIN, ISO9141, and UART are 39 to 10000000. Valid values for CGI are 115200 and 625000. Not applicable for any other network types.
Auto Bitrate Enable
Digital
Set to 1 to enable auto bitrate. Only supported for "first" two CAN channels of any 3G device.
CAN Tx Err Count
Analog
Number of CAN transmit errors on the network.
CAN Rx Err Count
Analog
Number of CAN receive errors on the network.
CAN Controller Mode
Analog
Controller mode if network is CAN. 0 - Normal 1 - Disabled 3 - Listen Only 7 - Listen All
CAN Transceiver Mode
Analog
Transceiver mode if network is CAN. 0 - Auto 1 - On 2 - Off 3 - High Voltage (SWCAN) 4 - High Speed (SWCAN)
CAN TQ SEG1
Analog
CAN time quanta for segment 1. Writing to this signal will change the Bitrate signal.
CAN TQ SEG2
Analog
CAN time quanta for segment 2. Writing to this signal will change the Bitrate signal.
CAN TQ Prop
Analog
CAN time quanta for propagation delay. Writing to this signal will change the Bitrate signal.
CAN Sync
Analog
CAN time quanta for synchronization jump width. Writing to this signal will change the Bitrate signal.
CAN BRP
Analog
CAN baud rate prescaler. Writing to this signal will change the Bitrate signal.
LIN Mode
Analog
Transceiver mode if network is LIN. 0 - Sleep 1 - Slow 2 - Normal 3 - Fast
LIN Master Resistor
Digital
Set to 0 to enable, 1 to disable. (This is not a typo!)
K-Line Message Termination
Digital
Selects how the end of frame is determined if network is K-Line, ISO9141, or Keyword 2000. 0 = Inner Frame Time 1 = GME CIM-SCL (GM Europe Column Integration Module - Steering Column Lock)
K-Line Checksum Enable
Digital
Set to 1 to enable auto appending the 8 bit checksum (byte sum of all bytes in frame). Also enables checksum validation in VSpy3/DLL.
K-Line Rx Inner Frame Spacing
Analog
Value depends upon K-Line Message Termination: If using Inner Frame Time: Value = 2 * P2 min ms (i.e. 50 = 2 * 25 ms) If using GME CIM-SCL: Value = 10 * "t_InterMessage min" ms (i.e. 3 = 10 * 0.3 ms)
K-Line Tx Inner Frame Spacing
Analog
Value depends upon K-Line Message Termination: If using Inner Frame Time: Value = 2 * P3 ms (i.e. 110 = 2 * 55 ms) If using GME CIM-SCL: Value = 10 * "Tx t_InterMessage" ms (i.e. 2 = 10 * 0.2 ms)
K-Line Tx Inner Byte Spacing
Analog
Value depends upon K-Line Message Termination: If using Inner Frame Time: Value = 2 * P4 ms (i.e. 10 = 2 * 5 ms) If using GME CIM-SCL: Value = 10 * "t_InterByte" ms (i.e. 1 = 10 * 0.1 ms)
K-Line Parity
Analog
Selects parity if network is K-Line, ISO9141, or Keyword 2000. 0 - None 1 - Even 2 - Odd
K-Line Enable Tester Resistor
Digital
Set to 1 to enable 510 ohm tester resistor if network is K-Line, ISO9141, or Keyword 2000.
CGI Checksum Enable
Digital
Set to 1 to enable 16 bit checksum if network is CGI.
CGI Rx Inner Frame Spacing (bits)
Analog
Sets receive message inner frame spacing (in bits) if network is CGI.
CGI Tx Inner Frame Spacing (bits)
Analog
Sets transmit message inner frame spacing (in bits) if network is CGI.
SWCAN AutoSwitch Resistor Enable
Analog
Enables SWCAN high speed mode. 0 = Disabled 1 = Autoswitch no resistor 2 = Autoswitch with resistor (default)
UART Tx Register
Analog
Stores data for transmitting on UART.
UART Tx Is Full
Digital
True if the UART transmit buffer is full.
UART Tx is Empty
Digital
True if the UART transmit buffer is empty.
UART Rx Register
Analog
Stores data received from UART.
UART Rx is Full
Digital
True if the UART receive buffer is full.
UART Rx is Empty
Digital
True if the UART receive buffer is empty.
UART Rx Parity Error
Digital
True if a UART parity error is detected.
UART Rx Frame Error
Digital
True if a UART frame error is detected.
UART Rx Overflow Error
Digital
True if a UART overflow error is detected.
UART Rx Clear FIFO
Digital
Clears the UART FIFO receive buffer when set to 1.
UART Error Field
Analog
Reports the Error Status of UART communication 1 = UART_NET_ERROR_TX_MISMATCH Rx does not equal Tx 2 = UART_NET_ERROR_TX_TIMEOUT no Tx ISR 4 = UART_NET_ERROR_TX_FIFO_OVERFLOW Tx FIFO overflow detected 8 = UART_NET_ERROR_RX_FIFO_OVERFLOW Rx FIFO overflow detected 16 = UART_NET_ERROR_RX_PARITY Parity error 32 = UART_NET_ERROR_RX_OVERFLOW Hardware overflow 64 = UART_NET_ERROR_RX_FRAME frame error
Node Properties
Count
Analog
Number of messages for the node.
Rate
Analog
Number of messages per second for the node.
Percent Use
Analog
Percent of network utilization for the node.
Max Rate
Analog
Maximum number of messages per second for the node.
Max Percent Use
Analog
Maximum network utilization for a node.
NetMgmt Frame Count
Analog
TBD
NetMgmt Is Simulated
Digital
TBD
Misc Data Items
GPS Items
GPS Altitude, Latitude, Longitude, Speed
Analog
GPS data values.
GPS Valid
Digital
True if GPS data is valid.
Input Items
Keyboard CTRL
Digital
True while keyboard control key is pressed.
Keyboard F6-F12
Digital
True while corresponding keyboard F6-F12 key is pressed.
neoVI PRO Buttons
Digital
True while corresponding neoVI PRO button is pressed.
Misc Items
Available Disk Space (KB)
Analog
Amount of disk space available, in kilobytes, at the Vehicle Spy exe file location.
Dropped Logged Sectors
Analog
Number of sectors dropped by the SD card logger.
neoVI PRO Outputs
Digital
Set true to activate the neoVI PRO LEDs, Backlight, Buzzer or invert its screen.
Sector Buffers Remaining
Analog
Number of sector buffers remaining. (CoreMini only) If the value is zero then there is no more buffering space for incoming messages. If you continue logging data you will cause a buffer overflow.
Time Items
Abs Time (Sec)
Analog
Absolute time since Vehicle Spy start button was pressed.
Day
Analog
Day of the month as set on the computer clock.
Day of week
Analog
Numbers 0-6 representing days of the week as set on the computer clock. 0=Sunday, 1=Monday, etc.
Hour
Analog
Hour from 0-23 as set on the computer clock. 0=Midnight, 12=Noon, etc.
Minute
Analog
Minute 0-59 as set on the computer clock.
Month
Analog
Month 1-12 as set on the computer clock.
Second
Analog
Second 0-59 as set on the computer clock.
Time (ms)
Analog
Millisecond value from the Windows TimeGetTime API.
Time Diff
Analog
Provides highly accurate (0.5 - 25 usec) message timing measurement in CoreMini. Basic script logic is: 1) Wait until both messages are present 2) Set TimeDiff = Msg2.AbsTime - Msg1.AbsTime 3) Set application signal = TimeDiff
Year
Analo
4 digit representation of the year as set on the computer clock.
Function Block Properties
Is Running
Digital
True when the function block is running. Works for any function block type.
Number Msgs Collected
Analog
Number of messages collected by a Capture function block.
MEP (Memory Edit Protocol) Properties
Value
Any
Value of the MEP signal. The data item type depends upon the MEP signal type defined in the A2L file.
Physical IO Properties
Analog Inputs
Analog Input 1-8
Analog
Reads Analog inputs on supported neoVI devices.
Analog Outputs
Analog Output 1-10
Analog
Sets the Analog outputs on supported neoVI devices.
General neoVI Hardware
Ain Report Interval
Analog
Report interval for analog inputs. (1 to 125 ms)
L Line State
Digital
Sets the L line state.
LED Flash Type
Digital
TBD
LED Group
TBD
TBD
Power Off Timer
Analog
Time (ms) since the last keep awake event occurred. (Rx msg, USB connect, etc.)
Power Off Timer Reset
Digital
Resets the Power Off Timer to 0.
Relay Group
TBD
TBD
Separation Time Offset
Analog
TBD
Tx Write Index
Analog
TBD
Tx Write Limit
Analog
TBD
Temperature Deg C
Analog
TBD
UART 1 Line State
TBD
TBD
UART 2 Line State
TBD
TBD
LEDs
LED 1-10
Digital
Set true to activate the selected LED. For FIRE, Red, Yellow, and ValueCAN3 hardware LED 1 = red and LED 2 = green.
LIN States
LIN1-6 State
TBD
TBD
Misc IO
Misc IO 1-67 Value
Analog
Sets or Reads the IO states for neoECU Chip.
Misc IO 1-67 Is Output
Digital
Sets the direction of IO on a neoECU Chip.
PWM Inputs
PWM Input 1-8 Value
Digital
Reads the Value of the Pulse to be sent for the duration sent with Pulse Width.
PWM Input 1-8 PWM Frequency (Hz)
Analog
Reads the Frequency of neoECU Devices that support PWM IO
PWM Input 1-8 PWM Duty (%)
Analog
Reads the Duty cycle of neoECU Devices that support PWM IO
PWM Input 1-8 PWM Pulse Width (us)
Ana
Reads the Pulse Width of neoECU Devices that support PWM IO
PWM Input 1-8 PWM Timer Source
Digital
Sets 16 bit timer source resolution for tracking pulse widths in firmware.
So, if pulses are wider than 1.6 ms use timer source value of 0. Firmware defaults timer source to 1.
PWM Outputs
PWM Output 1-8 Value
Digital
Sets the Value of the Pulse to be sent for the duration sent with Pulse Width.
PWM Output 1-8 PWM Frequency (Hz)
Analog
Sets the Frequency of neoECU Devices that support PWM IO
PWM Output 1-8 PWM Duty (%)
Analog
Sets the Duty cycle of neoECU Devices that support PWM IO
PWM Output 1-8 PWM Pulse Width (us)
Analog
Sets the Pulse Width of neoECU Devices that support PWM IO
PWM Output 1-8 PWM Timer Source
Digital
Sets 16 bit timer source resolution for tracking pulse widths in firmware.
So, if pulses are wider than 1.6 ms use timer source value of 0. Firmware defaults timer source to 1.
Power Management
Power Management Mode
Analog
Sleep mode of the neoVI hardware. (CoreMini only) 0 - Normal Sleep, Manual 1 - Normal Sleep, Timed 2 - Fast Wakeup, Timed 3 - Fast Wakeup, Manual
Power Management Network Enables
Analog
If Fast Wakeup is enabled, determines which network is using it. 0 = none 1 = HSCAN only 2 = MSCAN only 3 = HSCAN and MSCAN
Power Off Timer
Analog
Time (ms) since the last keep awake event occurred. (Rx msg, USB connect, etc.)
Power Off Timer Reset
Digital
Resets the Power Off Timer to 0.
Power Supply
Power Supply Current
Analog
N/A
Relays
Relay 1-8
Digital
Sets Relays on neoECU devices
Switches
Switch 1-8
Digital
Reads Switches on neoECU devices
neoVI FIRE Misc
CGI Bitrate
Analog
CGI network bitrate in bits per second (115200 or 625000). Read value represents the current bitrate. Write to signal to change desired bitrate.
CGI Enable
Digital
Set to 1 to enable the CGI network and disable conflicting networks.
Logging Buffer Index
Analog
Index of currently selected partition in SDCARD, used in CoreMini logging.
MISCIO Report Period
Analog
Report period (ms) of the input/output status message sent on the neoVI device virtual network.
Misc 3-6 Is Analog In
Digital
Sets if that MISC IO channel is an analog input or not.
Network Swap
Digital
Swaps HSCAN and MSCAN when enabled. Useful for applying an HSCAN script to MSCAN. 0 = normal (Tx HSCAN will show Rx on HSCAN) 1 = swapped (Tx HSCAN will show Rx on MSCAN)
Logger (CoreMini) Properties
Available Disk Space (kB)
Analog
Amount of SD card memory available, in kilobytes, at the CoreMini script location.
Dropped Logged Sectors
Analog
Number of sectors dropped by the SD card logger.
Is CoreMini
Digital
Reads as 1 if script is running in CoreMini, otherwise 0.
Logging Buffer Index
Analog
Index of currently selected partition in SDCARD, used in CoreMini logging.
Sector Buffers Remaining
Analog
Number of sector buffers remaining. (CoreMini only) If the value is zero then there is no more buffering space for incoming messages. If you continue logging data you will cause a buffer overflow.
Operators and Calculator Panel
There are many operators available in the Expression Builder. These are listed in Table 3 below. An operator can be added by selecting it from the list and then clicking the Add Operator button. Numbers can be added to your equation with the Calculator Panel (Figure 1:![]() ). Operators and numbers can both be added by typing them directly into the Expression field.
). Operators and numbers can both be added by typing them directly into the Expression field.
Table 3: Operators Available in the Expression Editor
+
Add
1+1 is 2
-
Subtract
1-1 is 0
*
Multiply
3*3 is 9
/
Divide
10/3 is 3.333333
^
Exponent
3^2 is 9
=
Equals
2=1 is False
>
Greater Than
5 > 3 is True
<
Less Than
5 < 3 is False
<>
Not Equal To
3 <> 32 is True
<=
Less Than or Equal To
5 <= 5 is True
>=
Greater Than or Equal To
6 >= 5 is True
>>(Arg)
Shift all bits to the right Arg times.
8 >> 1 is 4
<<(Arg)
Shift all bits to the left Arg times.
8 << 2 is 32
bitX(Arg)
Returns True if a specific bit is one
bit1(3) is True
byteX(Arg)
Returns a byte of a multi-byte value
byte0(256) is 0 byte1(256) is 1
one(Arg)
Returns 1 if Arg is true
One(5=5) is 1
and
Logical and Bitwise AND
(2=1) And (3=3) is False
or
Logical and Bitwise Or
(2=1) Or (3=3) is True
not
Logical and Bitwise Not
Not (1=1) is False
xor
Logical and Bitwise Xor
1 Xor 255 is 254
rnd(1)
Returns a random number between 0 and 1
Rnd(1) is 0.234324 (or other num)
abs(Arg)
Absolute Value of Arg
abs(-2) is 2
sin(Arg)
Sine of Arg (radians)
sin(3.141593) is 0
cos(Arg)
Cosine of Arg (radians)
cos(3.141593) is -1
tan(Arg)
Tangent of Arg (radians)
tan(0.785398) is 1
log(Arg)
Natural logarithm of Arg
log(2) is 0.6931471805
log10(Arg)
10 Based logarithm of Arg
log10(100) is 2
exp(Arg)
e (the base of natural logarithms) raised to a power
exp(2) is 7.3890560989
sqr(Arg)
Square root of arg
sqr(49) is 7
int(Arg)
Integer portion of arg
int(3.12434) is 3
mod
Divide two numbers and return only the remainder
19 Mod 6.7 is 5
arcsin(Arg)
Arcsine of Arg (radians)
arcsin(0) is 0
arccos(Arg)
Arccosine of Arg (radians)
arccos(-1) is 3.141593
arctan(Arg)
Arctangent of Arg (radians)
arctan(1) is 0.785398