FlexRay Controllers: State/Action Tab
The FlexRay Controllers State/Action tab is where the two FlexRay coldstart nodes within ICS hardware can be controlled and monitored. The tab is divided into Options, actions, and a node status table as shown in Figure 1.
Remember to select the correct Network above the tab before using any of the features.
Page navigation aids are included here to help with the long page length:
Options **** Actions **** Status Table **** States
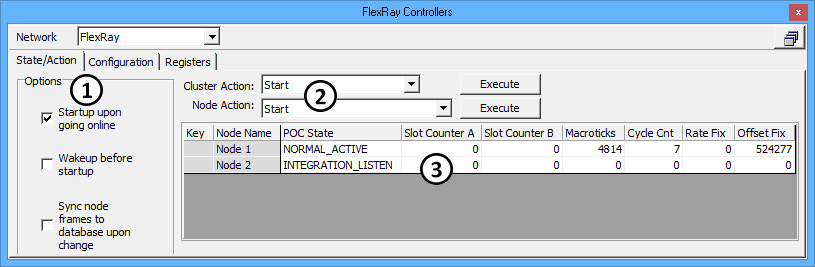
Options
The Options area (Figure 1:![]() ) includes some startup and synchronization settings. Additional options for synchronizing to a database are located at the bottom of the Configuration tab.
) includes some startup and synchronization settings. Additional options for synchronizing to a database are located at the bottom of the Configuration tab.
Table 1: State/Action Options
Startup upon going online
On - ICS hardware will be the "leading coldstart node", so it will coldstart the FlexRay cluster after going online with VSpy. Off - ICS hardware will be a "following coldstart node", so it will begin in a listen state after going online with VSpy. A startup from an external FlexRay node is needed before frames will appear.
Wakeup before startup
Startup upon going online must be ON before this feature will work. On - Each node within ICS hardware will transmit a FlexRay wakeup pattern on its wakeup channel after going online with VSpy, but before it does a coldstart. The wakeup pattern and channel are defined on the Configuration tab. A wakeup pattern must have at least two wakeup symbols to be successful. Off - ICS hardware will not send a FlexRay wakeup before doing a coldstart.
Sync node frames to database upon change
This setting can synchronize Messages Editor Transmit frames to the Database frames. On - After selecting an ECU in the Node Name list, all transmit frames assigned to that node are deleted and replaced with all database frames from the ECU. The ECUs and their database frames come from FIBEX or ARMXL files loaded in Network Databases. Off - Node transmit frames are not forced to be synchronized to a database.
FlexRay Wakeup and Coldstart
FlexRay wakeup and coldstart can be confusing, so they are explained further here.
A FlexRay cluster is a collection of at least two coldstart nodes and usually some non-coldstart nodes too. Coldstart nodes can start or join FlexRay cycling, but non-coldstart nodes can only join cycling.
FlexRay cycling begins if at least two coldstart nodes are awake and then one of them does a coldstart A node wakeup can come from an external trigger OR from a FlexRay wakeup sent by a coldstart node. A FlexRay wakeup is a pattern of at least two wakeup symbols sent on only one channel at a time. The entire cluster of nodes will wake up after detecting a FlexRay wakeup pattern on their wakeup channel, assuming the nodes were not already awake from their external triggers.
Cluster Action
ICS FlexRay hardware comes with two built-in nodes that can act as a simple cluster by itself or can be connected to a larger cluster of nodes. The cluster inside ICS hardware can be controlled on the State/Action tab by executing a Cluster Action (Figure 1:![]() ) while Vehicle Spy is online.
) while Vehicle Spy is online.
Table 2: Cluster Actions
Start
Forces the ICS hardware cluster to coldstart, which can also get an external cluster to begin cycling if the external cluster is already awake.
Stop
Forces the ICS hardware cluster to stop cycling, but this will not stop an external cluster that is already cycling.
Restart
Stops the cluster first before doing a Start.
Reconfigure and Restart
Reconfigures the ICS hardware cluster to the Configuration tab cluster settings, then forces the ICS hardware cluster to coldstart.
Node Action
There are many choices for a Node Action as described in Table 3 and most of them refer to specific controller states. Actions at this lower level are not usually needed unless trying to troubleshoot specific issues.
To perform a Node Action, select a node by highlighting its row in the status table, select a Node Action (Figure 1:![]() ), then click Execute to perform the selected action on the highlighted node.
), then click Execute to perform the selected action on the highlighted node.
It is strongly recommended to refer to state transition diagrams in the FlexRay Protocol 2.1A specification when using these node actions.
Table 3: Node Actions
Start
Forces node to coldstart.
Stop
Forces node to stop cycling. If POC state is NORMAL_ACTIVE then forces node to stop after the current cycle is done. (i.e. Halt) If POC state is not NORMAL_ACTIVE then forces node to immediately stop even if the current cycle is not done yet. (i.e. Freeze)
Restart
Stops the node first before doing a Start.
Reconfigure and Restart
Stops the node, then reconfigures it to Configuration tab node settings, then forces node to coldstart.
Set POC to Config
(POC means Protocol Operation Control, which is the FlexRay state control logic within the node.) Forces node state to DEFAULT_CONFIG or CONFIG depending upon when this action is attempted. Values are NOT configured until Node Action Perform Config of CHI and Msg Bufs is done.
Set POC to Ready
Forces node to be ready to send a wakeup, begin a coldstart, or jump into a cycling cluster.
Set POC to Wakeup
Forces node to send a wakeup pattern as defined on the Configuration tab.
Set POC to Monitor
Forces node to monitor for wakeups and cycling, but not send any frames itself.
Set POC to Halt
Forces node to stop cycling after the current cycle is done.
Set POC to Startup
Forces node to coldstart an inactive cluster or jump into a cycling cluster.
Set POC to Run
Forces a ready node to startup, otherwise does nothing.
Set POC to Freeze
Forces node to immediately stop cycling even if the current cycle is not done yet.
Set POC to Send MTS
Forces node to send a Media Access Test Symbol. The MTS is sent within a Symbol Window which is a cycle segment defined on the Configuration tab. Note: An MTS pulse is the same as a Collision Avoidance Symbol (CAS), but MTS is sent within a cycle and CAS is sent outside of a cycle.
Set POC to All Slots
Forces node from single slot mode to all slots mode. Single slot mode is an optional feature to limit frame transmission during startup.
Set POC to Reset Status Indicators
Resets node status flags that track coldstart and wakeup events. This action works only if the POC state is READY or STARTUP.
Set POC to Clear RAMs
Clears all POC related RAM in the node to zero. This action works only if the POC state is DEFAULT_CONFIG or CONFIG.
Perform Config of CHI and Msg Bufs
Forces node to configure its Controller Host Interface and message buffers. This action works only if the POC state is DEFAULT_CONFIG or CONFIG. If POC state is DEFAULT_CONFIG then settings come from "hardcoded" values stored within ICS hardware. If POC state is CONFIG then settings come from Configuration tab, Nodes branch settings.
State/Action Status Table
Each row in the status table (Figure 1:![]() ) represents one node in the ICS FlexRay hardware. A Vehicle Spy Cluster Action affects both nodes, but a Node Action only affects the selected node in the table.
) represents one node in the ICS FlexRay hardware. A Vehicle Spy Cluster Action affects both nodes, but a Node Action only affects the selected node in the table.
For each node, the status table shows the current logic state and timing location within the overall FlexRay cycle schedule. The status table also allows an ECU from a FlexRay database to be assigned to a node.
Table 4: State/Action Table
Key
Unused at this time.
Node Name
Name of the node as defined on the Configuration tab, Node Settings, ECU Short Name. Also, an ECU can be assigned to the node here if an ECU database from a FIBEX or ARMXL file is already loaded in Network Databases. This quickly allows ICS hardware to simulate a FlexRay ECU. WARNING: If the option Sync node frames to database upon change is ON then making an ECU selection here will replace all transmit frames assigned to the node with database frames from the selected ECU.
POC State
Current state of the FlexRay logic in the node. The many Protocol Operation Control states are described further in a table following this one. The node state can change due to external cluster connections or be changed directly by executing a Cluster or Node Action.
Slot Counter A
Current slot of channel A. Counter resets to 1 at the beginning of each cycle then counts slots across the static and dynamic segments until the end of the dynamic segment is reached.
Slot Counter B
Same counting logic as channel A, but this tracks channel B.
Macroticks
Current macrotick within the current cycle. Counter resets to 0 at the beginning of each cycle.
Cycle Cnt
Current cycle number that loops from 0 to 63.
Rate Fix
Current Rate Correction Value calculated by the node to adjust its macrotick frequency. Allows the node to compensate for internal clock drift and stay synchronized to a cycling cluster.
Offset Fix
Current Offset Correction Value calculated by the node to adjust its macrotick phase. Allows the node to compensate for internal clock drift and stay synchronized to a cycling cluster.
POC States
There are many Protocol Operation Control states that define FlexRay logic in a node. It is strongly recommended to refer to state transition diagrams in the FlexRay Protocol 2.1A specification when trying to understand the flow of these states.
A lookup table is included here for convenience, but this does not replace requirements from specifications. Most of this information is copied directly from the FlexRay 2.1A specification then edited for brevity. The states are listed alphabetically.
Table 5: POC States
ABORT_STARTUP
Exit cluster startup process for various reasons then get ready to try again by going to STARTUP_PREPARE.
COLDSTART_COLLISION_RESOLUTION
Detect and resolve collisions between multiple simultaneous coldstart attempts of several coldstart nodes.
COLDSTART_CONSISTENCY_CHECK
Leading coldstart node checks whether frames transmitted by other following coldstart nodes fit into its schedule.
COLDSTART_GAP
Leading coldstart node stops transmitting its startup frame. All nodes integrating on leading coldstart node will stop their integration attempt.
COLDSTART_JOIN
Only following coldstart nodes enter this state. Upon entry they begin transmitting startup frames and continue to do so in subsequent cycles.
COLDSTART_LISTEN
Coldstart node tries to detect ongoing frame transmissions and coldstart attempts. A coldstart node still allowed to initiate a coldstart enters this state before actually performing a coldstart.
CONFIG
Frame communication is stopped, all node configuration memory is accessible, and physical layer pins are set to their inactive state. Settings from the Configuration tab are applied.
DEFAULT_CONFIG
Frame communication is stopped, all node configuration memory is accessible, and physical layer pins are set to their inactive state. Default settings "hardcoded" in the firmware are applied.
HALT
Halts the node in preparation for reinitialization.
INITIALIZE_SCHEDULE
This state is entered as soon as a valid startup frame has been received in one of the listen states.
INTEGRATION_COLDSTART_CHECK
Only integrating coldstart nodes pass through this state. Verify clock can be corrected and leading coldstart node is still available.
INTEGRATION_CONSISTENCY_CHECK
Only integrating non-coldstart nodes pass through this state. Verify clock can be corrected and enough coldstart nodes are sending startup frames that agree with the node's own schedule.
INTEGRATION_LISTEN
Node waits for a valid startup frame or for a coldstart to be allowed.
MONITOR_MODE
Node receives wakeups and frames, but does not send any frames itself.
NORMAL_ACTIVE
Normal operation state following a successful startup. Node is synchronized to the cluster allowing continued frame transmission without disrupting other nodes. If synchronization problems occur, POC can transition to NORMAL_PASSIVE.
NORMAL_PASSIVE
Node can receive frames, but not transmit frames due to synchronization problems to the cluster. If synchronization improves, POC can transition back to NORMAL_ACTIVE. If synchronization problems persist, POC transitions to HALT.
READY
Node is ready to send a wakeup, coldstart a cluster, integrate into an ongoing cluster, or be configured again.
STARTUP_PREPARE
Node prepares to listen for cluster activity.
STARTUP_SUCCESS
This seems to not really be a POC state, but is actually a critical flag that must be true to enter the NORMAL_ACTIVE state.
WAKEUP_DETECT
Node attempts to identify reason for wakeup collision detected in WAKEUP_SEND state then returns to WAKEUP_STANDBY.
WAKEUP_LISTEN
Node prepares to quickly send a wakeup in a noise free scenario or waits a bit longer in a noisy environment.
WAKEUP_SEND
Node sends wakeup pattern on wakeup channel defined on the Configuration tab. Node transitions to WAKEUP_DETECT if collisions are detected.
WAKEUP_STANDB
Node is waiting to send a wakeup pattern.
Page navigation aids are included here to help with the long page length:
Options **** Actions **** Status Table **** States **** Top of Page****